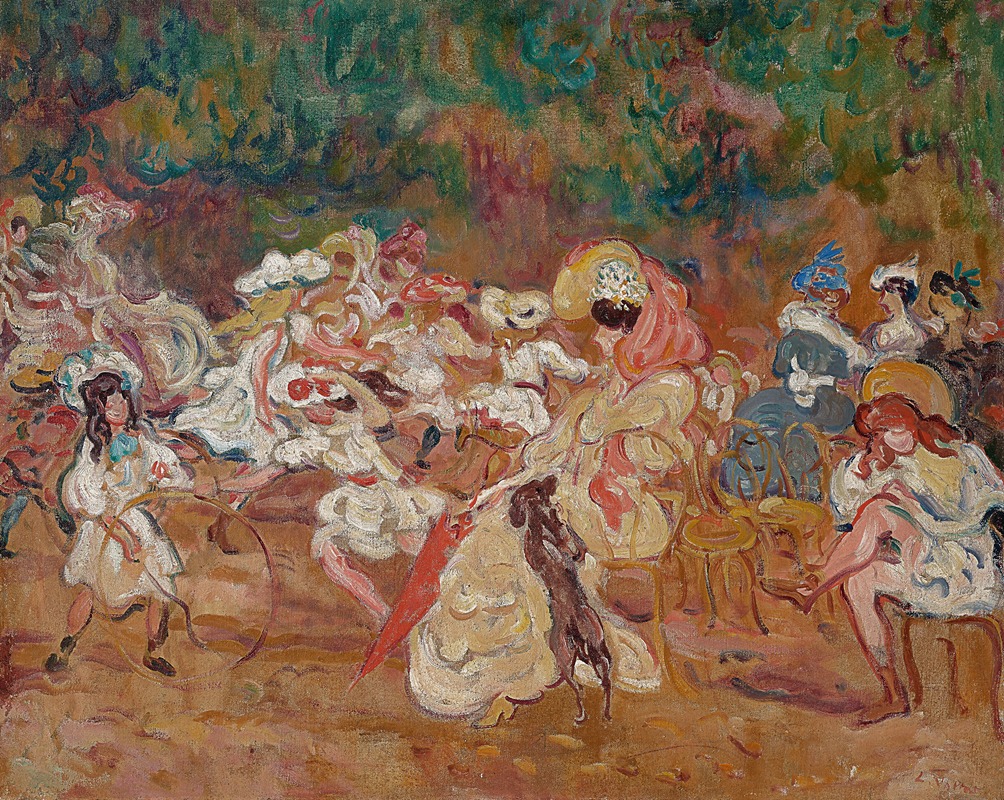
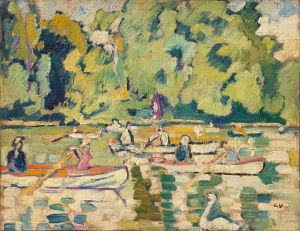Jeux d’enfants
A hand-painted replica of Louis Valtat’s masterpiece Jeux d’enfants, meticulously crafted by professional artists to capture the true essence of the original. Each piece is created with museum-quality canvas and rare mineral pigments, carefully painted by experienced artists with delicate brushstrokes and rich, layered colors to perfectly recreate the texture of the original artwork. Unlike machine-printed reproductions, this hand-painted version brings the painting to life, infused with the artist’s emotions and skill in every stroke. Whether for personal collection or home decoration, it instantly elevates the artistic atmosphere of any space.
Louis Valtat was a French painter associated with the Post-Impressionist movement, known for his vibrant use of color and expressive brushwork. Born in 1869 in Dieppe, France, Valtat was a contemporary of artists like Pierre Bonnard and Édouard Vuillard, and he played a significant role in the transition from Impressionism to Fauvism. His work often depicted scenes of everyday life, landscapes, and still lifes, characterized by bold colors and dynamic compositions.
"Jeux d’enfants" (translated as "Children's Games") is one of Valtat's notable works, capturing the innocence and joy of childhood through his distinctive artistic style. The painting exemplifies Valtat's ability to convey movement and emotion, using a vivid palette that brings the scene to life. While specific details about the creation date or the current location of "Jeux d’enfants" are not widely documented, it is consistent with Valtat's broader body of work from the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Valtat's approach to painting was heavily influenced by his education at the École des Beaux-Arts and the Académie Julian in Paris, where he was exposed to the avant-garde movements of the time. His early works were influenced by Impressionism, but he gradually developed a more personal style that incorporated elements of Fauvism, characterized by the use of non-naturalistic colors and bold brushstrokes.
In "Jeux d’enfants," Valtat likely employed these techniques to create a lively and engaging scene. The painting would typically feature children engaged in playful activities, rendered in a manner that emphasizes their spontaneity and energy. The use of color in Valtat's work is particularly noteworthy, as he often employed contrasting hues to create a sense of depth and vibrancy, drawing the viewer's eye across the canvas.
Valtat's contribution to the art world extends beyond his paintings. He was part of a circle of artists who were instrumental in the development of modern art in France. His work was exhibited alongside that of other prominent artists of the time, and he participated in several important exhibitions, including the Salon des Indépendants and the Salon d'Automne.
Despite his significant contributions, Valtat's work did not achieve the same level of fame as some of his contemporaries during his lifetime. However, his paintings have gained recognition in the years following his death in 1952, appreciated for their innovative use of color and form.
"Jeux d’enfants" remains a testament to Valtat's skill in capturing the essence of his subjects, offering a glimpse into the playful world of children through the lens of a master colorist. His ability to blend elements of Impressionism and Fauvism has secured his place in the history of modern art, and his works continue to be studied and admired for their artistic merit and historical significance.